How is Trichomonas colpitis transmitted? Symptoms and treatment of trichomonas colpitis in women and men
Trichomoniasis is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections. According to statistics, about 10% of the population of all countries suffer from this disease. Trichomonas have a number of features that allow them to go undetected for a long time, even during examination. How does infection occur and how to suspect the disease? Are there effective treatment regimens?
Read in this article
How is Trichomonas colpitis transmitted?
The disease is caused by Trichomonas vaginalis. These are single-celled organisms that can only exist in the human body.
- When exposed to the environment, they quickly die, even under normal room conditions. The following factors are especially detrimental to them:
- high temperatures (over 45);
- direct sunlight;
- change in osmotic pressure;
When they come into contact with household items, they quickly dry out and die.
Based on this, the main route of transmission of infection is sexual, in unprotected intimate relationships.
- They can be found in the following places:
- in the vagina and cervical canal in women most often;
- they can also penetrate into the uterine cavity and appendages, sometimes causing the appearance of abscesses and tubo-ovarian formations;
in the urethra, bladder, and less often in other parts of the urinary tract.
Theoretically, a contact-household route is also possible, for example, infection through towels, in a bathhouse, or through other hygiene products. But in practice you don’t have to deal with this.
Factors contributing to the development of trichomoniasis
- Often, trichomoniasis can occur in subclinical forms, causing virtually no complaints. In this case, the following circumstances may contribute to the manifestation of the disease:
- Decreased immunity due to stress, hypothermia, physical activity, etc.
- During the period after infectious diseases, exacerbation of chronic pathology.
- Alcohol (and even beer), spicy, salty, pickled, can also slightly increase the symptoms of diseases.
Taking hormonal medications, in particular glucocorticosteroids, as well as certain medications, for example, for chemotherapy.
Symptoms of Trichomonas colpitis
- Copious vaginal discharge. It can be white or transparent, as well as greenish, yellowish, swampy, and others. It all depends on whether there is a concomitant infection. Blood may also be present, especially if there is erosion. It is believed that the discharge is always foamy, since trichomonas emit carbon dioxide during their life processes. But this can only be noticed during a gynecological examination, and not always.
- A burning sensation that may be unusually red and swollen.
- Frequent relapses, the appearance of condylomas are all evidence of immunodeficiency due to infection.
- The woman also notes periodic nagging pain in the lower abdomen, which can intensify during sexual intercourse.
- If your body temperature rises, it means that the inflammation has spread beyond the vagina. There is a possibility of dissemination of the infection and the development of abscesses, pyosalpings, even peritonitis.
- Inflammation of the urinary system. Most often these are cystitis and urethritis, including recurrent ones.
Consequences of untreated colpitis
Trichomonas colpitis is insidious. This is due to the following factors:
- Trichomonas can be recognized by the body as its own cells. In this case, it does not respond to them with the proper inflammatory process, which allows the infection to remain undetected for a long time.
- Trichomonas have an amazing property - they can “swallow” other pathogens and maintain their activity for a long time. Most often, myco- and ureaplasmas, and some others, “hide” this way. As a result, during treatment, pathogens are incompletely eradicated, or they become resistant to drugs (antibiotics). So the process gradually becomes chronic.
Thus, it is important not only to treat Trichomonas colpitis in a timely manner, but also to be examined in parallel for other infections. But it is better to prevent infection with reliable means of protection during sexual intercourse.
Trichomonas colpitis can lead to the following complications:
- Pathology of the cervix (erosion, etc.). Trichomonas play a significant role in development.
- Inflammation of the endometrium with all the ensuing consequences (hyperplasia, polyps, etc.), pyosalpings, pyovariums. Episodes of Trichomonas pelvioperitonitis occur regularly.
- Problems with pregnancy - from the inability to conceive to fading at different stages, premature birth, intrauterine infection, etc.
Watch the video about trichomonas colpitis:
Diagnosis of trichomoniasis
You can suspect the presence of Trichomonas colpitis based on complaints and gynecological examination. But the following methods are used for confirmation:
- Common from the posterior vagina. It is ideal if the doctor takes the material and looks at it right away, even without staining. Trichomonas are mobile, so their activity can be easily seen under a microscope. More often, the material is simply applied to a glass slide and then sent to the laboratory.
- An oncocytology smear also detects pathogens if they are present in the cervical canal.
- The most reliable method for determining Trichomonas is PCR. At the same time, you can be examined for other sexually transmitted infections with one sample.
- The cultural method (inoculation on a medium) is practically not used, as it is superseded by the price range, ease of execution and effectiveness of PCR.
Treatment of trichomonas colpitis
Despite the fact that trichomoniasis is one of the most common infections, the range of drugs for treatment is not very wide.
Since this pathology very often occurs together with other STIs, it is highly advisable to conduct a full examination before starting therapy; only one sexual partner is possible.
The basics of therapy are as follows:
- It is mandatory to take tablets orally, i.e. systemic effect on the body;
- it is advisable to combine with suppositories, vaginal capsules, etc.;
- treatment of other sexually transmitted infections is carried out in parallel;
- results must be monitored by both sexual partners, and not earlier than 2 - 3 weeks from the end of therapy. Women should get tested on the eve of menstruation, since at this time immunity decreases, and if the infection is not completely cured, it will somehow manifest itself at this time.
It is very easy to get trichomoniasis, but it is not always possible to get rid of these microorganisms the first time. Often the infection becomes subclinical.
At the same time, Trichomonas seem to stop their vital activity, and it seems that a complete cure has occurred. But with provoking factors, the symptoms of the disease reappear.
Drug therapy
| The most effective are the following groups of drugs: | Drugs |
| Application | Metronidazole and its analogues (Trichopol, Klion-D, Metrogyl, Metron, Flagyl and others) Approximate regimen: 0.5 g of metronidazole twice a day plus 0.5 g of the drug vaginally. If this is a treatment for a man, the entire dose is for internal use. The duration of treatment is 10 - 14 days. |
| Tinidazole (Fasigil and others) | It is also highly sensitive to these pathogens and is available in the form of 500 mg tablets. Its advantages over metronidazole are shorter treatment regimens. For example, you can drink 2 g of the drug once and that’s it. |
| Clindamycin is an antibiotic with antiprotozoal activity. | Most often used in combination with metronidazole. Included in the preparations Dalacin, Clindacin, Zerkalin and others. There are both tablets for oral administration, vaginal cream, and suppositories. Approximate treatment regimen: 300 mg of the drug for 10 days in any form. |
The following drugs also have anti-trichomonas activity: iodine-based (Betadine, Povidone-iodine, etc.), hydrogen peroxide, chlorhexidine and some others. They are used mainly in early pregnancy to reduce the harmful effects on the baby. Metronidazole is considered relatively safe only from the 20th week of gestation.
How to treat chronic trichomoniasis
Incomplete compliance with prescribed regimens often leads to the development of chronic forms of trichomoniasis. Treatment in this case consists of the same drugs, but they are taken for a longer time.
Vaccination against trichomoniasis using Solcotrichovax is particularly effective. This technique is used at all stages of trichomoniasis. The vaccine allows you to get rid of pathogens, normalize the vaginal flora, and also prevent re-infections.
In the treatment of chronic trichomoniasis, it is most effective to combine local and general pathogenetic therapy against the background of vaccination with Solcotrichovax.
ethnoscience
There are many traditional medicine methods to combat trichomoniasis. However, it is better to combine this treatment with drug therapy, otherwise the disease can become chronic.
Recipe 1. It is beneficial to take garlic juice several times a day. 1 - 2 teaspoons per dose is enough.
Recipe 2. You should take flowers of lilac, calendula, bird cherry and celandine herb in equal quantities. Pour all 200 ml of hot water and let it brew for about half an hour. Douching should be done with the resulting solution.
Recipe 3. It is useful to use sea buckthorn oil to put into the vagina on a gauze pad. It has an anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial effect, relieves swelling and itching.
Recipe 4. You should take horseradish root and chop it. Pour boiling water over and let it brew for about an hour. Use for douching.
Prevention of trichomonas colpitis
The main prevention of trichomoniasis is the use of barrier contraception during sexual intercourse. You should also be vigilant when going to baths, saunas and never use other people’s intimate hygiene products.
You should regularly visit a gynecologist, even in the absence of complaints, and strictly follow the prescribed treatment regimens for all diseases.
Trichomonas colpitis is a common sexually transmitted infection, which is quite difficult to treat and can become chronic.
Ignoring the problem can lead to serious health problems, even precancerous conditions. Trichomoniasis is also dangerous during pregnancy. Therefore, it is important to promptly diagnose and treat the infection.
Trichomonas colpitis is an inflammatory process in the vagina caused by a protozoan organism of the flagellate class (Trichomonas), which is transmitted sexually through the male urethra. This infection multiplies very quickly in a moist environment, attaches to the walls of the vaginal mucosa, and then penetrates inside.
In addition to sexual transmission, there is a possibility of infection during everyday situations (using other people's towels, underwear), as well as during oral sex. But the greatest likelihood of contracting Trichomonas colpitis is through traditional sex.
Classification of the disease
- Trichomonas colpitis can be divided into 2 types.
- Spicy. With it, symptoms appear unexpectedly. Sharp itching in the vagina, the appearance of pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen, the appearance of purulent and bloody discharge with an unpleasant odor. The walls of the vagina are inflamed and painful when in contact with anything. Sometimes they may bleed if examined carelessly. In this case, the infection is likely to spread into the uterine cavity. The nature of the disease depends on the individual characteristics of the woman, her age, immunity and the type of infectious agent. During Trichomonas colpitis, many women also note the presence of purulent-foamy discharge with a pungent odor.
Chronic. If a woman delays treatment or tries to carry it out on her own, colpitis can become chronic. In this case, the infection becomes sluggish, with periodic exacerbations. In this case, the infection may spread deep into the uterus, which can often lead to the removal of the tubes and uterus.
The inflammatory process in the vagina in girls is called vaginitis. It usually manifests itself in the form of redness of the outer labia, itching, swelling and spotting of a purulent nature. Acute colpitis in girls can be a result of serious illnesses, poor hygiene and a foreign body entering the vagina.
Symptoms
The hidden feature of this disease is that some may not even suspect that they are a carrier of this virus. When one partner appears to be in good health, the other may clearly show signs of Trichomonas colpitis. In addition, due to the frequent presence of ureoplasma viruses, gonococci, mycoplasma and chlamydia, treatment becomes very difficult. In order to avoid serious consequences and protect yourself from complications, you need to visit a doctor at the first symptoms of infection. If the signs are not identified on your own, then for the purpose of prevention and to ensure that you are not a carrier of the virus, a visit to the doctor should occur every 6 months. Our specialists will help you with this.
Trichomonas colpitis in women is manifested by the following symptoms:
- the appearance of thick discharge, often foamy (this is due to the ability of Trichomonas to produce carbon dioxide). The color of the discharge may be cloudy white, greenish or brown. Often you can see blood or even pus in them. The specific smell can be compared to the smell of rotten fish;
- the appearance of nodes or condylomas on the labia. This occurs due to a decrease in the immune system due to chronic illness;
- unbearable itching in the vagina, the skin is hot when touched, possibly bleeding;
- discomfort and heaviness in the lower abdomen;
- painful and problematic urination;
- high temperature, weakness, drowsiness. Stomach upset may also occur;
- menstrual irregularities, delayed menstruation;
- discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse, lack of orgasm.
Trichomonas colpitis in women can also occur due to frequent stress, climate change, long-term use of medications, and a sudden change in diet. A previous serious illness can also affect the detection of this disease.
Trichomonas colpitis suffered during pregnancy can cause changes in hormonal levels and a disruption in the activity of the immune system.
Trichomonas colpitis may show its symptoms either in the early stages or not at all.
Trichomonas colpitis after menopause
This type of colpitis is also called atrophic. This occurs due to changes in a woman’s hormonal background and a sharp decrease in hormones in the blood. As a result of this, the vaginal mucosa loses its former balance and becomes less protected from external and internal factors. Loss of lactobacilli levels during postmenopause makes the vaginal flora potentially vulnerable to inflammation.
The variety of types of infections can be confusing. The symptoms of many of them are very similar, so you need to see a doctor for a correct diagnosis. Correct diagnosis is the basis of treatment!
Treatment
Antitrichomonas drugs are used in the treatment of this disease. In this case, furatsilin, gramicidin and others are used. In this case, it is also necessary to carry out general health procedures for the vaginal and uterine mucosa. It is equally necessary to strengthen the immune system in general.
Treatment is considered complete, and the woman is healthy only when a smear analysis 3 months in a row after the menstrual cycle reveals the absence of Trichomonas. Each time, the analysis is taken on the first, second and third days after the end of menstruation.
Prevention
To protect yourself from this serious disease, you do not need to be a professional gynecologist. It is enough just to know the basic rules of personal hygiene. This disease (like many other sexually transmitted diseases) does not require prophylactic medication, you just need to know certain rules:
- never use other people’s towels, linen and other personal items;
- avoid casual sex and unsafe sex;
- avoid sexual contact with people susceptible to diseases such as HIV (alcoholics, drug addicts, homosexuals).
In the event that contact with an unfamiliar person does occur, and even without protective equipment, you should immediately perform the following actions:
- you should urinate as soon as possible;
- wash the vagina thoroughly with an intimate cleanser;
- treat the vagina and labia with miramistin solution.
If you begin to increasingly notice itching in the perineum, discomfort when moving, pronounced pain in the lower abdomen and discomfort during sex, you need to immediately visit a gynecologist.
Some people prefer to treat this condition at home. Do not forget that a trip to the doctor should be inevitable. And traditional medicine can only become an additional treatment with the basic recommendations of a doctor. Like all other diseases, trichomonas colpitis requires immediate treatment.
Or vaginitis, an inflammation of the vaginal mucosa caused by the single-celled protozoan bacterium Trichomonas. The most common cause of the disease is the entry of the pathogen into the vagina during unprotected sexual contact with a male carrier of the infection. Trichomonas attaches to the cells of the vaginal mucosa, multiplies quickly in a humid and warm environment, the field of which penetrates deep into the epithelium.
In more than 80% of all cases, infection occurs through sexual contact, and extremely rarely through household means: when using hygiene items after a carrier of the infection. In the external environment, the pathogen remains stable for no longer than 3 hours, so this cause of the disease is mainly theoretical and practically never occurs.
Frequent changes of sexual partners and neglect of condoms increase the risk of developing Trichomonas colpitis by 4 times. The following factors also contribute to the development of the disease:
- endocrine disorders;
- decreased immunity;
- physical exhaustion;
- hypothermia;
- chronic stress;
- treatment with corticosteroids, consequences of chemotherapy, etc.
In almost 90% of patients, trichomonas is accompanied by a concomitant infection - fungi, gonococci, chlamydia, staphylococci, ureaplasma and mycoplasma.
Symptoms of Trichomonas colpitis
With trichomonas colpitis, patients complain:
- abundant foamy vaginal discharge of yellow or green color, with an unpleasant odor, sometimes with purulent or bloody impurities;
- itching and burning in the genital area;
- frequent and painful urination;
- redness and swelling of the external genitalia;
- pain during and after sexual intercourse;
- fever, general weakness, temporary diarrhea, nagging pain in the lower back;
- menstrual irregularities.
In advanced forms of the disease, genital warts may appear in the perineal area.
Diagnosis of Trichomonas colpitis
The doctor makes a preliminary diagnosis during a physical examination. To confirm it, smears are taken from the vagina (sometimes also from the rectum). The pathogen is identified using one of the laboratory tests:
- bacteriological culture;
- cytology method.
According to indications, the gynecologist can refer the woman to a dermatovenerologist and urologist.
Treatment of trichomonas colpitis
The goal of treatment is to eliminate the pathogen and inflammation. The classic therapeutic regimen includes oral antibiotics and the use of local antiseptics - vaginal suppositories and douching solutions. The doctor selects the drug and its dosage individually.
Both sexual partners undergo the therapeutic course at the same time to prevent re-infection. During treatment, it is necessary to avoid sexual intercourse and alcohol consumption. The effectiveness of therapy is monitored by taking repeated vaginal smears - immediately after the course and after 3 menstrual cycles. The sexual partner also takes a control test.
After treatment, eubiotic drugs are prescribed to restore the vaginal microflora according to indications. To increase the body's defenses, immune stimulating agents can be prescribed.
Prevention
To prevent infection with Trichomonas colpitis, you must:
- use a condom during sexual intercourse with an untested partner;
- avoid casual sex;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- avoid hypothermia;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- be examined by a gynecologist at least 2 times a year;
- carry out all medical prescriptions.
Complications
As a rule, Trichomonas colpitis causes discomfort and significantly worsens the quality of life, so in most cases patients consult a doctor in a timely manner. In rare cases of the disease without symptoms, as well as in attempts at self-medication, pathological microflora fills the vagina and affects other pelvic organs, causing complications.
Trichomonas colpitis is an inflammatory disease of the mucous membranes of the vagina and urinary tract. The pathology is provoked by trichomonas infection - one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases. Infection occurs during unprotected sexual contact, and in 80% of cases this is sexual intercourse with unfamiliar partners. The disease is easily diagnosed - its symptoms cannot be confused with anything else, and the pathogen is easily detected in a smear on the flora. The danger lies in the fact that the microorganism quickly spreads to surrounding tissues, and patients do not immediately seek medical help and try to solve a delicate problem by self-medication. In the acute phase, the disease is easily treatable, while the chronic form requires complex multi-stage treatment.
Causes
In adult sexually active women, trichomonas colpitis can have only one cause - transmission of trichomonas (Trichomonas vaginalis) as a result of unprotected sexual intercourse. Trichomonas remain viable in a humid environment at a temperature of +37 ° C; in other conditions they die in 2–3 hours. Therefore, if tests show the presence of Trichomonas in the body, you should not hope that the infection occurred through extrasexual contact. Theoretically, this possibility exists, but cases are observed mainly in girls upon contact with contaminated underwear or washcloths, as well as in newborns from infected mothers. Some strains of Trichomonas cause characteristic symptoms, others develop asymptomatically, but can manifest themselves in a sexual partner if infected.
Once in the body, Trichomonas secrete a toxin that helps them protect themselves from cells of the immune system and poisons surrounding tissues. The stronger the mucous membrane resists infection, the more pronounced the symptoms. With weak immune defense, inflammation occurs in a subacute manner.
In women, Trichomonas colpitis as a monoinfection occurs only in 10.5% of cases. Basically, Trichomonas are combined with chlamydia, staphylococci, gardenella, ureaplasma, gonococci, fungi and other pathogenic microorganisms, for which they create a kind of reservoir protected from the immune system.
Symptoms
Symptoms of Trichomonas colpitis appear on the third to fifth day after sexual contact with a patient or a carrier partner. When taking antibiotics or having problems with the immune system, signs are sometimes detected two weeks after infection. The disease can have an acute or chronic course.
The acute form of the disease is accompanied by specific symptoms, which are determined during the initial examination. These include the symptoms presented below.
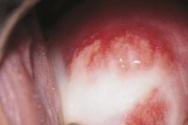
- Copious leucorrhoea of a foamy nature with an unpleasant odor. With monoinfection they have a yellowish tint, with the addition of other pathogenic microorganisms they have a greenish tint, and with inflammatory damage to small blood vessels, ichorous inclusions appear in the leucorrhoea.
- Itching, burning and discomfort in the mucous membranes of the vagina and vulva, as well as severe swelling of damaged tissues, which causes pain during intimate contact.
- Inflammatory phenomena of other organs of the genitourinary system. Trichomonas can move independently, causing inflammation in the urethra and bladder, cervical canal, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries.
During a visual examination of the vagina, the gynecologist may note signs of acute inflammation. This is swelling and hyperemia of the mucous membranes, their loose texture, bleeding after contact with instruments, foamy discharge with an unpleasant odor on the walls and in the vaults of the vagina, possible pinpoint hemorrhages. In cases of severe acute inflammation, the surface of the cervix may resemble a strawberry in appearance.
Symptoms in the chronic form are less pronounced. The amount of leucorrhoea is insignificant, irritation of the vagina and vulva is mild. The disease may not cause any inconvenience, but will be transmitted through intimate contact and cause complications in the carrier. From this point of view, the chronic form is considered the most unfavorable.
To diagnose chronic Trichomonas colpitis, an analysis of vaginal, urethral or cervical canal discharge will be required using bacterial culture, ELISA, or PCR. Trichomonas can be found as a monoinfection or as part of a microbial association.
The disease can have serious consequences during pregnancy. The infection can penetrate the tissues surrounding the fetus and cause inflammation, provoke premature labor, rupture of water, and lead to the birth of a low-weight fetus.
Treatment
Treatment of trichomonas colpitis includes stopping the acute infectious process and complete destruction of trichomonas. In women, treatment is also prescribed to the sexual partner, since as long as he is a carrier of the infection, re-infection is inevitable.
Therapy for the disease includes local and systemic drugs (in early pregnancy - only locally). The most effective against trichomonas is Metronidazole and its analogues - Timorazole, Trichopolum, Flagyl, Tinidazole, etc. The duration of use and dosage are prescribed by the doctor depending on the results of laboratory tests. Terzhinan, Klion D, Trichomonacid and others suppositories, which are inserted into the vagina before bedtime, can be used as local remedies. It is also possible to use ointments, gels and douching solutions of a similar composition.
When treating trichomonas colpitis in chronic form, additional use of immunomodulators, probiotics and absorbable drugs is required. All this is necessary to restore local immunity.
Ten days after the start of treatment, the patient undergoes a control examination, and then repeated examinations during two monthly cycles. If all tests show a negative result, the woman is considered healthy.
Prevention
Since there is no specific immunity to Trichomonas, the only measure to prevent this type of STD is to avoid unprotected sexual contact with partners who may be carriers of the infection. It is necessary to either completely abstain from casual sex or use condoms. During unprotected sexual intercourse, the external genitalia and inner thighs should be treated with Miramistin solution, and a tampon soaked in this product should be inserted into the vagina.
In recent decades, the number of sexually transmitted diseases has increased sharply. Doctors believe that the reason for this is a rather early initiation into sexual activity, as well as low sexual culture and education of the population. One of the most common infections is trichomoniasis, which occurs in the form. This disease not only brings the patient a lot of unpleasant sensations, but is also a direct threat to further pregnancy and childbirth. That is why it is so important to know the first symptoms of the disease and consult a doctor in time.
What is trichomonas colpitis
Trichomonas colpitis is an infectious disease accompanied by inflammatory changes in the vaginal mucosa. Most often, the causative agent of trichomoniasis enters the body through unprotected sexual intercourse and direct contact with a carrier of the pathology.
Less common are cases of transmission of the microbe through the use of personal hygiene products or underwear shared with the patient, or when transferred from insufficiently processed medical or cosmetic equipment. The disease can appear even after a single contact with the pathogen, since it only takes a few seconds for its penetration.
Trichomonas colpitis is a particular form of damage to the vaginal mucosa. In men, trichomoniasis occurs with similar symptoms, which differ due to the anatomical structure of the genital organs.
Existing varieties of the disease
- Classification of pathology according to the nature of the course:
- acute colpitis (rapid increase in symptoms over 1–2 days, intoxication and fever);
- subacute (less pronounced clinical picture that develops within a week to a month);
chronic (periodically occurring exacerbations against the background of short or long-term remission, the disease exists in the body for more than six months).
- Varieties of the disease depending on the attachment of foreign microflora to Trichomonas:
- combined with bacteria (gardnerella, mycoplasma, ureaplasma);
- combined with viruses (herpes, HPV).
Video: doctor talks about pathology
Why does Trichomonas colpitis develop?
The leading cause of the disease is infection with Trichomonas. This pathogen is a tiny microorganism in the form of a drop, which has several flagella at its end. Such elements provide high mobility and protect Trichomonas from the effects of cells of the human immune system.
Trichomonas is a simple microbe that has several flagella for movement.
Factors that increase the likelihood of infection:
- promiscuity;
- other diseases of the urogenital tract (chlamydia, candidiasis, gonorrhea);
- inflammatory processes in the pelvic area;
- frequent visits to beauty parlors and hair removal specialists;
- violation of personal hygiene rules and use of other people's things;
- stagnation of venous blood in the lower half of the body;
- recently undergone surgery with the installation of a urinary catheter;
- uncontrolled use of antibacterial drugs;
- primary or secondary immune deficiency.
Video: Elena Malysheva talks about trichomoniasis
Main clinical manifestations of pathology
All sexually transmitted diseases have a fairly specific symptomatic picture. Often, Trichomonas colpitis develops gradually, as a result of which women do not always consult a doctor in a timely manner. In some cases, an asymptomatic course is possible, when the disease is detected only during a routine examination or when taking a smear.
In people with weakened immune systems, the main symptoms of the disease intensify with a cold or flu. This is directly related to the slow metabolic processes occurring in the human body.
Clinical manifestations of Trichomonas colpitis:
- Changes in the external genitalia. As inflammation develops, the lips major and minor increase in size and swell. The mucous membrane becomes more sensitive and thin, even minor irritation leads to the formation of tiny cracks and tears. During sexual intercourse or insertion of a tampon, due to a lack of natural lubrication, sharp pain occurs, and injuries are typical.
- The occurrence of pathological discharge. They usually have an unpleasant smell of rotten fish or spoiled meat, bubble and accumulate on the laundry. When it dries, it forms a sticky crust that is quite difficult to remove. The amount of discharge varies depending on the patient’s lifestyle: with active sexual intercourse, physical activity or stress, it increases sharply. Color can vary from dark brown to gray and yellow. The appearance of bloody impurities indicates the destruction of blood vessels and the formation of a hematoma.
- Unpleasant pulling sensation in the lower abdomen. In part, they resemble menstrual pain, but they occur on any day of the cycle. Psycho-emotional stress, overeating or alcohol abuse leads to an increase in this symptom. For pain relief, 1-2 tablets of Ketorol are usually enough, after which the discomfort weakens or completely disappears.
Photo gallery: symptoms of the disease
 Inflammation is always accompanied by swelling and redness of soft tissues
Inflammation is always accompanied by swelling and redness of soft tissues  Abdominal pain is nagging
Abdominal pain is nagging  Pathological discharge may have different colors
Pathological discharge may have different colors
Trichomonas colpitis and pregnancy
When carrying a baby, a woman's body undergoes hormonal changes. This leads to increased vulnerability of the mucous membranes to the action of various microbes. That is why, during the period of waiting for a child, many chronic ailments sharply worsen, and the patient begins to feel worse. Symptoms of the disease in pregnant women are practically no different from the course of the pathology in other women: the amount of discharge increases slightly, and the child may experience long-term consequences of infection (retarded growth and development, lack of amniotic fluid).
Methods for diagnosing the disease
To identify Trichomonas colpitis, you need to contact a gynecologist. To begin with, the doctor conducts a general examination and examines the condition of the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix. Women are required to be asked the number of pregnancies, births, abortions and miscarriages, as well as the methods of contraception used.
Often, trichomonas lesions of the vaginal mucosa are masked behind other infections. I had the opportunity to participate in the examination of a woman with obvious signs of thrush - she was bothered by itching, and periodically there was a whitish discharge. After examining a tissue sample, it turned out that candida microflora suppressed the symptoms of trichomoniasis, but it could only be cured with antibiotics.
Methods for identifying the disease:
- microscopic examination of the smear allows you to identify the causative agents of infection (they look like small drop-shaped microbes with flagella);
- identifying the sensitivity of microflora to antibiotics helps doctors select the necessary drug for treatment;
- polymerase chain reaction - the newest method for determining pathogen DNA in biological material using a centrifuge;
- An ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs shows the presence of fluid in the uterine cavity and pathological adhesions in the tubes, which indicates a chronic process.
Table: differential diagnosis of trichomonas colpitis and other gynecological pathologies
| Comparative characteristics | Trichomonas colpitis | Gonorrhea | Thrush | Ureaplasmosis | Syphilis |
| Changes in the external genitalia | Swelling, irritation of the mucous membrane | Minor redness and itching of soft tissues | Formation of whitish plaque on the labia majora and minora | None | The appearance of lumps and lumps with ulceration and decay of soft tissues |
| Nature of the discharge | Brown-yellow mixed with blood, viscous and thick | Green, swampy, stick to underwear | White or yellowish, plentiful, have a cheesy consistency | Transparent or gray, sticky | Dark brown or black |
| Vaginal odor | Pungent smell of spoiled fish | Unpleasant putrid odor | Sour milk smell | Not found or weakly expressed | Absent |
What does discharge look like for various urogenital ailments?
 Thrush discharge has a cheesy consistency
Thrush discharge has a cheesy consistency  Discharge from trichomonas colpitis is accompanied by a fishy odor
Discharge from trichomonas colpitis is accompanied by a fishy odor  Discharge from gonorrhea is purulent in nature
Discharge from gonorrhea is purulent in nature
Various treatment options for trichomonas colpitis
Diseases of the reproductive system require immediate treatment immediately after confirmation of the diagnosis. In mild cases, doctors limit themselves to prescribing a gentle diet and using medications for external treatment of the vagina. If the pathology has gone quite far, physiotherapy and systemic medications are used. At all stages of treatment, a woman must observe a certain hygienic regime and regularly visit a gynecologist.
Timely monitoring will allow you to track effectiveness and change the scheme if necessary.
Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of illness Treatment of Trichomonas colpitis is carried out in several directions at once. Doctors need to completely relieve the patient of discomfort, remove the causative agent of infection and prevent relapses. All products are divided into local ones, which are applied to the mucous membranes or inserted into the vagina, as well as general ones, taken in the form of capsules, tablets, powders or injections.
The course of treatment for trichomoniasis is intended for two. Therapy of the sexual partner is a mandatory step that will prevent the circulation of the pathogen in the couple.
Preparations for local treatment of mucous membranes:
- Antiseptic solutions help remove excess secretions and clean the vagina. For this purpose, Miramistin, Furacilin, Chlorhexidine, Chlorophyllipt are used. This treatment is used before applying ointments or inserting tampons or suppositories.
- Antibacterial drugs cause the death of pathogenic microbes, disrupting the growth and reproduction of Trichomonas. The most common medications: Terzhinan, Hexicon, Nystatin, Meratin Combi, Neotrizol, Flucostat.
- Means for normalizing vaginal microflora are used in parallel with a course of antibiotics. They promote the revival of beneficial bacteria, which independently fight infection and also prevent the occurrence of injuries. Most often, doctors prescribe: Vaginorm-S, Acylact, Gynoflor E, Laktonorm, Lactobacterrin, Vagilak.
Photo gallery: medications for local treatment of mucous membranes
 Miramistin is available with a special dispenser, which is convenient to insert into the vagina
Miramistin is available with a special dispenser, which is convenient to insert into the vagina  Terzhinan is the best remedy to combat Trichomonas
Terzhinan is the best remedy to combat Trichomonas  Vagilak prevents the development of cracks
Vagilak prevents the development of cracks
Drugs for systemic treatment of the disease:
- General antimicrobial drugs are used for massive damage to the mucous membrane. These include Streptomycin Sulfate, Azithromycin, Zhalacin, Rifampicin, Levorin, Nystatin, Polymyxin M sulfate, Natamycin, Clindamycin, Azithromycin, Roxithromycin, Cefpirome, Amoxiclav, Neomycin sulfate.
- Steroid anti-inflammatory medications can quickly get rid of swelling, itching and irritation. The most common substances in this group: Prednisolone, Dexamethasone, Cortef, Laticort, Dexazone, Dexona, Polcortolone, Sinaflan, Medopred, Kenalog.
- Painkillers relieve discomfort in the pelvic area. For this purpose, Ketorol, Nimesulide, Ibuprofen, Tramal, Tramadol, Analgin are used.
Photo gallery: drugs for systemic therapy
 Amoxiclav is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that destroys bacteria
Amoxiclav is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that destroys bacteria  Prednisolone reduces soft tissue swelling
Prednisolone reduces soft tissue swelling  Analgin quickly relieves pain
Analgin quickly relieves pain
Traditional medicine as an additional remedy
Unfortunately, it is often possible to get an appointment with a gynecologist only a week after making an appointment, and the symptoms continue to increase and bother patients. If you do not have access to private doctors, you should use traditional recipes to alleviate the manifestations of Trichomonas colpitis. Decoctions, infusions, baths and lotions can get rid of the signs of the disease, but do not eliminate the cause that caused it.
Therefore, doctors strongly advise not to give up traditional medicine, even if you feel relief.
Some folk recipes are not intended for use on the vaginal mucosa. In my practice, I had the opportunity to participate in the treatment of a woman who received a severe chemical burn. On the Internet, the victim found a remedy to combat the inflammatory process on the skin - celandine tincture. The patient soaked a cotton swab generously in this liquid and placed it into the vagina. Within a few minutes, the woman felt a severe burning sensation, and the removed tampon was covered in blood. After calling an ambulance, the victim was hospitalized in the gynecology department, where an emergency operation was performed. As it turned out, the celandine juice corroded the blood vessel, as a result of which the woman almost died from hemorrhagic shock. This is why doctors recommend not using high-intensity products for mucous membranes.
- Popular recipes to combat the manifestations of trichomonas colpitis:
- Dissolve 2 tablespoons of baking soda in a glass with 0.5 liters of boiling water. After cooling, draw the solution into a syringe and rinse the vaginal cavity several times. It is believed that soda has an antiseptic effect and allows you to create an environment unfavorable for the further growth and development of pathogenic microorganisms. But such douching, if abused, leads to vaginal dryness: the procedure should be done once a week before bedtime.
- Boil 50 grams of hop cones and 30 grams of cherry leaves over low heat in a liter of water. After cooling, soak a gauze pad in the liquid, squeeze it out to remove excess, and then insert it into the vagina for 10–30 minutes. This technique allows you to get rid of itching and burning, and also softens the mucous membrane. You can use this method every day.
Photo gallery: folk remedies for the treatment of inflammation
 Calendula relieves inflammatory swelling
Calendula relieves inflammatory swelling  Hop cones reduce itching and burning
Hop cones reduce itching and burning  Soda creates an unpleasant environment for trichomonas
Soda creates an unpleasant environment for trichomonas
Video: disease therapy with herbs
Features of nutrition of patients with trichomonas colpitis
The diet also helps victims in the fight against diseases of the urogenital tract. Many pathogenic microorganisms, including Trichomonas, feed on fast carbohydrates entering the patient’s digestive system. That is why, when fighting colpitis of this nature, it is recommended to reconsider your usual eating style. Doctors advise avoiding fatty, fried, smoked foods high in oil and salt. Instead, foods should be boiled, stewed or baked using only olive oil.
For Trichomonas colpitis, you must drink at least 2 liters of water per day. You should give up coffee, black tea, carbonated drinks and packaged juices, as well as alcohol at least for the period of treatment.
What foods should be included in the diet:
- Adyghe cheese and goat milk;
- cottage cheese, whey; kefir, yogurt without additives, fermented baked milk, bifidok;
- lean meat and fish (especially river fish);
- mussels, shrimp, squid;
- fresh vegetables, fruits and berries in the form of salads, fruit drinks, smoothies, cocktails;
- lean soups;
- porridge and cereals;
- legumes and peas;
- durum pasta;
- greenery;
- nuts;
Photo gallery: healthy food
 Spinach is rich in vitamins and microelements
Spinach is rich in vitamins and microelements  Nuts contain many amino acids and healthy fats
Nuts contain many amino acids and healthy fats  Oatmeal is the best source of slow carbohydrates
Oatmeal is the best source of slow carbohydrates
Personal hygiene rules for victims
Sanitation of the vagina is an integral stage in the treatment of trichomonas colpitis. Before applying any drug, it is necessary to remove pathological secretions and protect the mucous membrane from traumatic effects. For this purpose, syringes are used - small bulbs with a rubber or plastic tip.
 The syringe can be purchased at the pharmacy
The syringe can be purchased at the pharmacy Rules for the procedure:
- Rinse the device using intimate hygiene gel and dry thoroughly with a towel. If you are using a syringe for the first time, it makes sense to boil it over low heat for a few minutes.
- Treat the nozzle with an antiseptic (hydrogen peroxide is suitable) and draw in the medicine. Insert the tip into the vagina and douche until the fluid released becomes clear.
- Rinse the pear several times and place in a dry and warm place. Remember to change the device every few months to prevent bacteria from growing inside.
How to use tampons to treat the inflammatory process:
- Wipe the external genitalia with a gauze pad soaked in water. Douche.
- Remove a clean swab from the package and apply the medication. Try to distribute the medication evenly. Wait for 2-3 minutes until the drug is completely absorbed.
- Gently insert the tampon into the vagina (use an applicator if necessary). After 10–40 minutes, remove it. If discomfort occurs while wearing, you can change the position with clean hands.
Features of treatment of chronic form of Trichomonas colpitis
With a long course of the disease, harmful microorganisms become resistant to traditional antibacterial drugs. This leads doctors to choose more effective regimens from a combination of several antimicrobial drugs, and also resort to other methods of therapy.
One of the effective ways to combat the chronic form of Trichomonas colpitis is physical therapy.
- What procedures help with the disease:
- Ultrahigh frequency therapy. With the help of a special apparatus, currents of varying intensity enter the woman’s body. They stimulate the activity of the circulatory system and improve metabolic processes in the body, as a result of which the formation of adhesions slows down.
- Massages. The doctor acts precisely on certain points of the female body using mechanical force. This helps to normalize venous and lymphatic outflow, which allows you to effectively remove toxins from the damaged area.
- Electrophoresis is the introduction of medications into the patient’s body using current. Electrodes are placed in the abdomen, through which the pharmaceutical quickly penetrates the blood vessels and spreads throughout the body. The effect occurs within 10–15 minutes, and the procedure itself is completely painless, which provides its advantage over injections.
Photo gallery: physiotherapy to combat illness
 Electrophoresis ensures faster introduction of medicine into the body
Electrophoresis ensures faster introduction of medicine into the body  Magnetic therapy helps reduce pain
Magnetic therapy helps reduce pain  Ultrahigh frequency therapy reduces the risk of infertility
Ultrahigh frequency therapy reduces the risk of infertility
Treatment prognosis and probable negative consequences of the pathology
Trichomonas colpitis is an extremely serious and dangerous form of infectious lesion of the genital organs. Its treatment can take from 2–4 months to 1.5–3 years, depending on the severity of the case. Restoring reproductive function and preparing the body for pregnancy lasts another year. If the disease was detected in the later stages of development, this process may extend indefinitely. The older a woman is, the less likely she is to give birth to a healthy baby after suffering a trichomonas infection.
If the victim has other diseases of the reproductive system (genital herpes, gardnerellosis, gonorrhea, syphilis, candidiasis), then it will take much more time to rehabilitate the body. This is directly related to impaired metabolic processes and slower regeneration of soft tissues.
The patient’s recovery is largely influenced by a responsible approach to following medical recommendations. Doctors prescribed one woman to undergo a course of antibacterial therapy together with her partner, who was the source of the infection. The girl was embarrassed to tell her man about the problem and was treated alone, while continuing to have sex with a carrier of trichomoniasis. Re-infection occurred, but under the influence of antibiotics the infection became chronic. The slow course of the inflammatory process and the subsequent proliferation of connective tissue provoked the appearance of adhesions in the fallopian tubes. A few years later, in the process of planning a pregnancy, the girl encountered problems with conception: the embryo was formed in the tubes, and not in the uterus. The only solution was artificial insemination.
What complications may occur in patients with Trichomonas colpitis:
- miscarriage (abortion, miscarriage);
- improper attachment of the fetus (in the tubes, ovaries, abdominal cavity);
- proliferation of connective tissue constrictions;
- intrauterine infection of a child;
- premature birth;
- fetal malformations;
- the appearance of ovaries;
- the formation of inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs;
- amputation of the uterus along with appendages;
- irritation and hypersensitivity of the vaginal mucosa;
- damage to the bladder sphincter and urinary incontinence.
Photo gallery: possible complications of the disease
 Adhesions are the main cause of infertility in women
Adhesions are the main cause of infertility in women  Polycystic ovary syndrome is a disruption of the normal structure of the organ due to the proliferation of pathological formations
Polycystic ovary syndrome is a disruption of the normal structure of the organ due to the proliferation of pathological formations  Premature baby has abnormally low body weight and needs resuscitation
Premature baby has abnormally low body weight and needs resuscitation  Urinary incontinence treated with sling surgery
Urinary incontinence treated with sling surgery
How to protect your body from Trichomonas infection
Diseases of the reproductive system have an extremely negative impact on the reproductive function of the female body. The main goal of obstetricians-gynecologists is to preserve the health of each patient with the possibility of subsequent childbearing.
That is why the problem of preventing Trichomonas colpitis is especially acute for doctors. Doctors are confident that it is necessary to teach girls the rules of personal and sexual hygiene from a very young age, which will allow them to avoid unprotected sexual intercourse and other problems.
During my internship in the obstetrics and gynecology department, I had the opportunity to participate in annual preventive medical examinations. Women assigned to this clinic were required to undergo a full examination once a year. All patients had smears taken to determine the purity of the microflora, and the presence of pathogenic microorganisms was also determined. As it turned out from the test results, about 20% of all women have any manifestations of trichomonas colpitis, and another 10% are asymptomatic carriers of the causative agent of the disease. Doctors conducted a separate conversation with the victims, during which it turned out that most of them use hormonal pills, suppositories, IUDs or interrupted sexual intercourse as a method of contraception, even with an unfamiliar partner. These methods of protection contributed to the spread of urogenital infections. All women were given coupons for further consultation with a specialist to prescribe a course of therapy. After only 4 months, many of them noted a significant improvement in the situation at their follow-up appointment.